Gravitation, Formelsammlung
Verfasst: Di 1. Dez 2015, 23:47
In Arbeit
1) Newton
Zeit t, Integral:
}} \, \text{d}r)
Zeit t, analytisch:
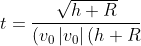-2 G M)^{3/2}} \cdot ...)
+2 G h M} \sqrt{R v_0 \left| v_0\right| (h+R)-2 G M R}+\right. ...)
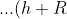 \left(\sqrt{\left| v_0\right| } \sqrt{v_0 (h+R)} \sqrt{v_0 \left| v_0\right| (h+R)-2 G M}+\right. ...)
-\sinh ^{-1}\left(\sqrt{\frac{v_0 \left| v_0\right| (h+R)}{2 G M}-1}\right)\right)\right)\right))
Zeit t, numerisch:
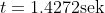
Gesamtgeschwindigkeit v, Integral:
 \, dr})
Gesamtgeschwindigkeit v, analytisch:
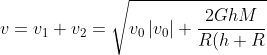}})
Gesamtgeschwindigkeit v, numerisch:
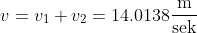
Einzelgeschwindigkeiten v1 & v2:
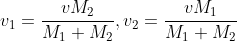
Strecke statt Ziel:
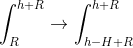
Hier ist h die initiale Höhe und H die bereits gefallene Strecke.
.nb
1) Newton
Code: Alles auswählen
(* Gegeben *)
G = 667384*^-16 m^3/kg/sek^2; (* Newtons Konstante *)
M1 = 5972 10^21 kg; (* Erdmasse *)
M2 = 1 kg; (* Testmasse *)
M = M1 + M2; (* Gesamtmasse *)
R1 = 6371000 m; (* Erdradius *)
R2 = 1 m; (* Objektradius *)
R = R1 + R2; (* minimaler Schwerpunktabstand *)
h = 10 m; (* Fallhöhe *)
v0 = 0 m/sek; (* Initialgeschwindigkeit *)
(* Gesucht *)
t = f[\!\(
\*SubsuperscriptBox[\(\[Integral]\), \(R\), \(R + h\)]\(
\*FractionBox[\(1\),
SqrtBox[\(2\ G\ M\ \((
\*FractionBox[\(1\), \(r\)] -
\*FractionBox[\(1\), \(R + h\)])\) +
v0\ Abs[v0]\)]] \[DifferentialD]r\)\)] (* Fallzeit, integriert *)
t = f[1/(-2 G M + (h + R) v0 Abs[v0])^(3/2) Sqrt[
h + R] (-Sqrt[2 G h M + R (h + R) v0 Abs[v0]] Sqrt[-2 G M R +
R (h + R) v0 Abs[v0]] + (h +
R) (Sqrt[(h + R) v0] Sqrt[Abs[v0]]
Sqrt[-2 G M + (h + R) v0 Abs[v0]] +
2 G M (ArcSinh[Sqrt[-(R/(h + R)) + (R v0 Abs[v0])/(2 G M)]] -
ArcSinh[
Sqrt[-1 + ((h + R) v0 Abs[v0])/(
2 G M)]])))] (* Fallzeit, analytisch *)
v = f[Sqrt[\!\(
\*SubsuperscriptBox[\(\[Integral]\), \(R\), \(R + h\)]\(\((
\*FractionBox[\(2\ G\ M\),
SuperscriptBox[\(r\), \(2\)]] +
\*FractionBox[\(v0\ Abs[
v0]\), \(h\)])\) \[DifferentialD]r\)\)]] (* insgesamte Geschwindigkeit, integriert *)
v = f[Sqrt[(2 G M h)/(R (R + h)) +
v0 Abs[v0]]] (* insgesamte Geschwindigkeit, analytisch *)
v1 = v M2/(M1 + M2) (* Geschwindigkeit Erde *)
v2 = v M1/(M1 + M2) (* Geschwindigkeit Objekt *)Zeit t, Integral:
Zeit t, analytisch:
Zeit t, numerisch:
Gesamtgeschwindigkeit v, Integral:
Gesamtgeschwindigkeit v, analytisch:
Gesamtgeschwindigkeit v, numerisch:
Einzelgeschwindigkeiten v1 & v2:
Strecke statt Ziel:
Hier ist h die initiale Höhe und H die bereits gefallene Strecke.
.nb