Kerr Metric
Verfasst: Do 12. Apr 2018, 22:24

 This is the english version.
This is the english version.  Deutschsprachige Version auf kerr.yukterez.net und Yukipedia.
Deutschsprachige Version auf kerr.yukterez.net und Yukipedia.

Shadow and surfaces of a spinning black hole (a=1), click to enlarge (png). Zoom out: [-], Contours: ƒ, Raytracing Code: ▤


Shadow and surfaces of a spinning black hole (a=0.99), Animation parameter: polar angle (θ=1°..90°). Slower: ⎆


Accretion disk with inner radius ri=isco and outer radius ra=7 around a BH with a=0.95, observer at r=100, θ=70°

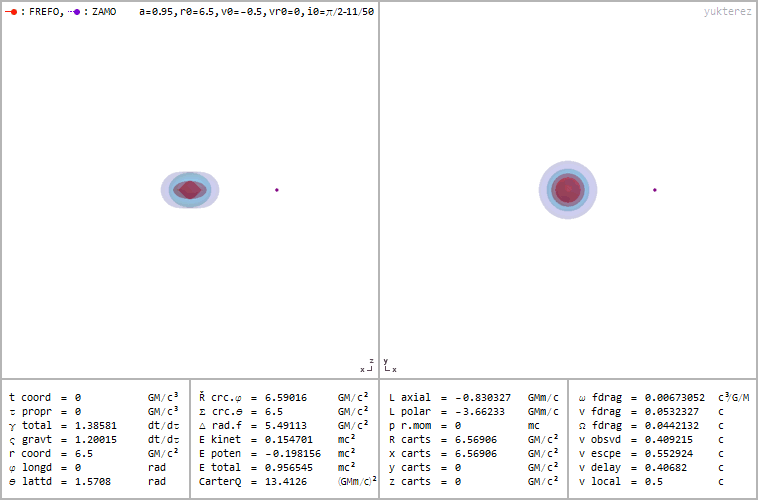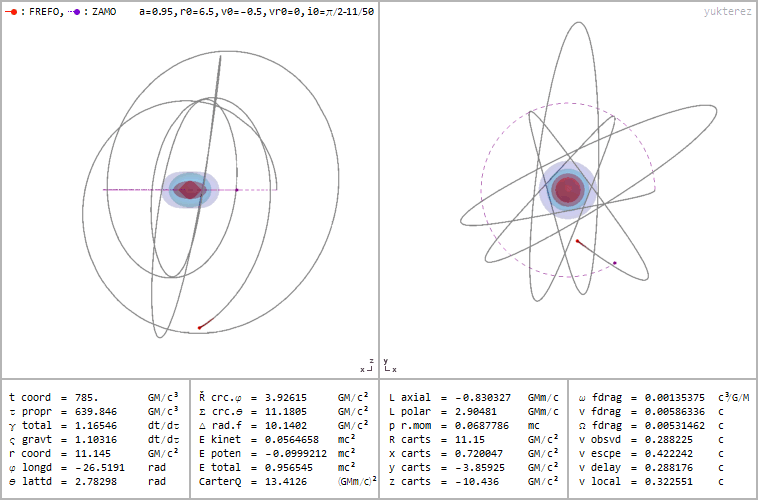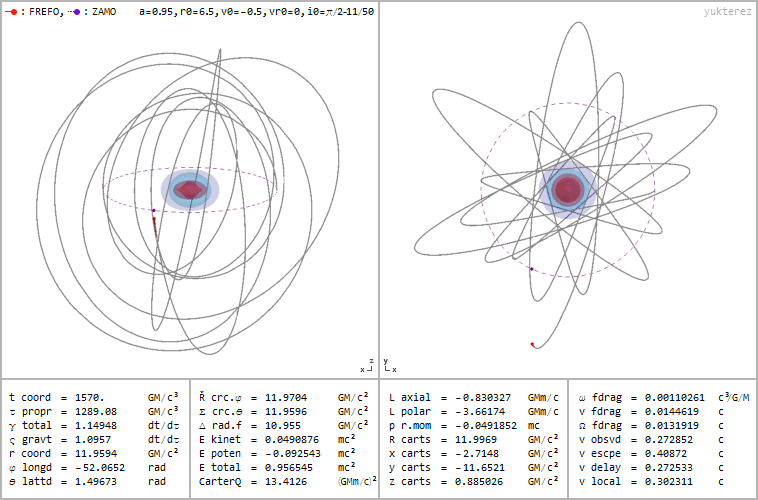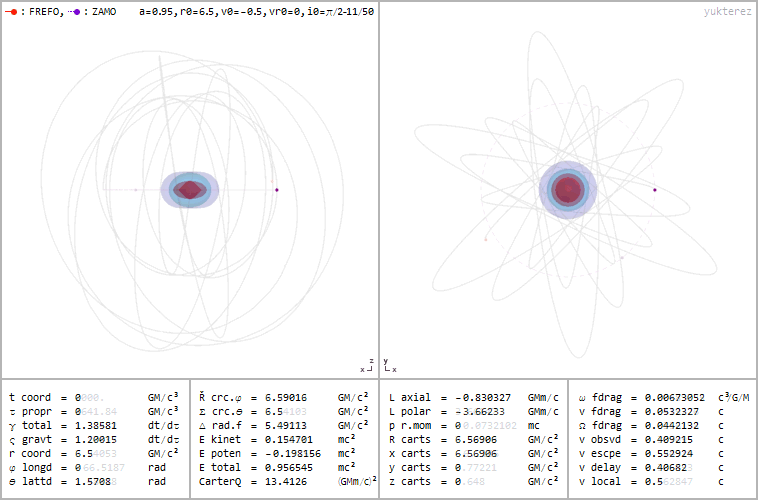
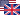
Retrograde orbit of a particle around a spinning black hole (a=0.95), coordinates: cartesian

Here we use natural units of G=M=c=1, so lengths are in GM/c² and times in GM/c³. The metric signature is time-positive (+,-,-,-). a is the spin parameter (for black holes 0≤a≤M), M the mass equivalent of the total energy of the black hole, and Mirr its irreducible mass:


Shorthand terms:
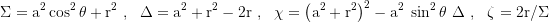
Covariant metric coeffizients:

Contravariant components (superscripted letters are not powers, but indices):

The dimensionless spin parameter is a=Jc/G/M². Transformation into cartesian coordinates:
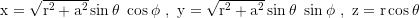
Line element in Boyer Lindquist coordinates:

Metric tensor (t,r,θ,Ф):

With a=0 Boyer Lindquist coordinates reduce to classical Schwarzschild coordinates.

With the transformation:

where T is a finkelsteinlike time coordinate (radially infalling photons move with dr/dt=1) and ψ the flattened azimuthal angle:
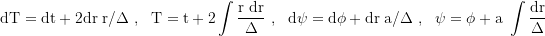
the metric in Kerr Schild coordinates (T,r,θ,ψ) is:
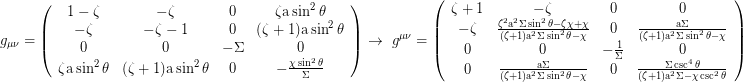
With a=0 Kerr Schild coordinates reduce to Eddington Finkelstein coordinates.

Equations of motion in Boyer Lindquist coordinates

Canonical four-momentum components:
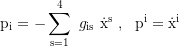
Coordinate time by proper time (dt/dτ):

First proper time derivative of the radial coordinate (dr/dτ):

Radial momentum derivative:
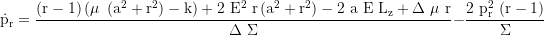
Radial momentum:
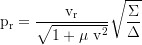
Derivative of the poloidial (longitudinal) component of motion (dθ/dτ):
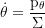
Derivative of the poloidial angular momentum (dpθ/dτ):
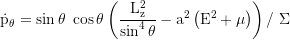
Axial (latitudinal) angular momentum:

Derivative of the axial component of motion (dФ/dτ):

Axial angular momentum derivative (pФ/dτ):
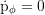
Axial component of the angular momentum:
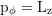
Constant of motion, Carter's constant:
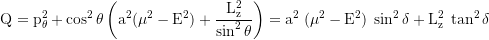
Constant of motion, Carter k:
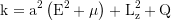
Constant of motion, total energy:
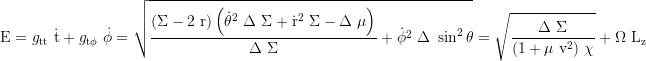
Constant of motion, axial angular momentum:
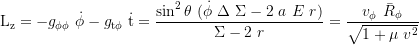
Local 3-velocity component along the r-axis:
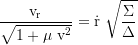
Local 3-velocity component along the θ-axis:

Local 3-velocity component along the Ф-axis:
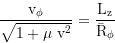
Local 3-velocity, total:

For massive testparticles μ=-1 and for photons μ=-0. δ is the inclination angle. With α as the vertical launch anglel the components of the local velocity (relative to a ZAMO) are

Shapirodelayed and frame dragged velocity as observed at infinity:

The radial effective potential which defines the turning points is:

Radial escape velocity:


Frame-Dragging angular velocity oberserved at infinity (dФ/dt):
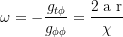
Delayed Frame-Dragging transverse velocity at the equator of the outer horizon:

with the horizons and ergospheres (solution for r at Δ=0 and gtt=0):

r and θ dependend delayed Frame-Dragging transverse velocities:

at the equatorialen plane at θ=π/2:

r und θ dependend local Frame-Dragging transverse velocities (greater than c inside of the ergosphere):

at the equatorialen plane at θ=π/2:

Cartesian projection of the Frame-Dragging transverse velocity:

at the equatorialen plane at θ=π/2:

Gravitational time dilation component relative to a ZAMO (dt/dτ):
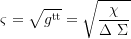
Axial and coaxial radius of gyration:
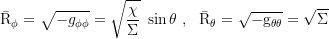
Axial and coaxial circumference:

The innermost stable orbit (ISCO) is at

with the shorthand terms


For images and animations see the german version of this site.